
#Second law of thermodynamics calculator download
All thermodynamic source data is available for download in standard formats. The database is coupled to a web interface that enables users to perform thermodynamic calculations with ease. eQuilibrator houses a collection of measured and approximated thermodynamic data. Indeed, that is exactly what eQuilibrator is. The most reliable way to perform these calculations is by using a well-tested computer program with access to a comprehensive and accurate database of thermodynamic data. This work is straightforward, but also arduous and error-prone. Reaction energies must be transformed to physiological conditions by applying metabolite concentrations, pH and ionic strength values from the literature. Care must be taken to ensure that the various data sources used are compatible with each other and that all reactions analyzed are properly balanced. For example, consider a simple thermodynamic question: in which direction does the fructose bisphosphate aldolase reaction in glycolysis proceed when all reactants are present in 1 mM concentrations at pH 7.5 and ionic strength 0.2? To answer this question, thermodynamic parameters must be retrieved from the literature. It can be quite time-consuming to apply thermodynamic analyses to a pathway or reaction of interest. For example, recent work engineering Escherichia coli for 1,4-butanediol production leveraged thermodynamic analysis to highlight the most promising candidate pathways and to eliminate those unlikely to flow to 1,4-butanediol ( 7). Therefore, a metabolic reaction or pathway can be subjected to thermodynamic analysis to determine whether it is feasible under physiological conditions and which conditions enable it to produce the desired outputs ( 6, 10). The cellular conditions-temperature, pH, ionic strength, concentrations of metabolites and ions, etc.-can significantly affect the thermodynamic feasibility of a particular reaction direction. That is, the change in Gibbs energy due to a reaction (Δ r G) must be negative.īiochemical reactions have context: they take place inside cells. In these metabolic research and engineering efforts it is essential to account for thermodynamic constraints: chemical reactions can sustain flux in a given direction only if they lead to a reduction in the Gibbs energy ( G). More recently, metabolic models have succeeded in accurately predicting bacterial growth modes and biologists have succeeded in designing and implementing novel biosynthetic pathways for the production of fuels and other valuable chemicals ( 5–9). The metabolic networks of numerous organisms have been studied in detail as well as their responses to changes in internal and external conditions ( 1–4). The structure and function of cellular metabolism has been a central area of biological inquiry for over a century.
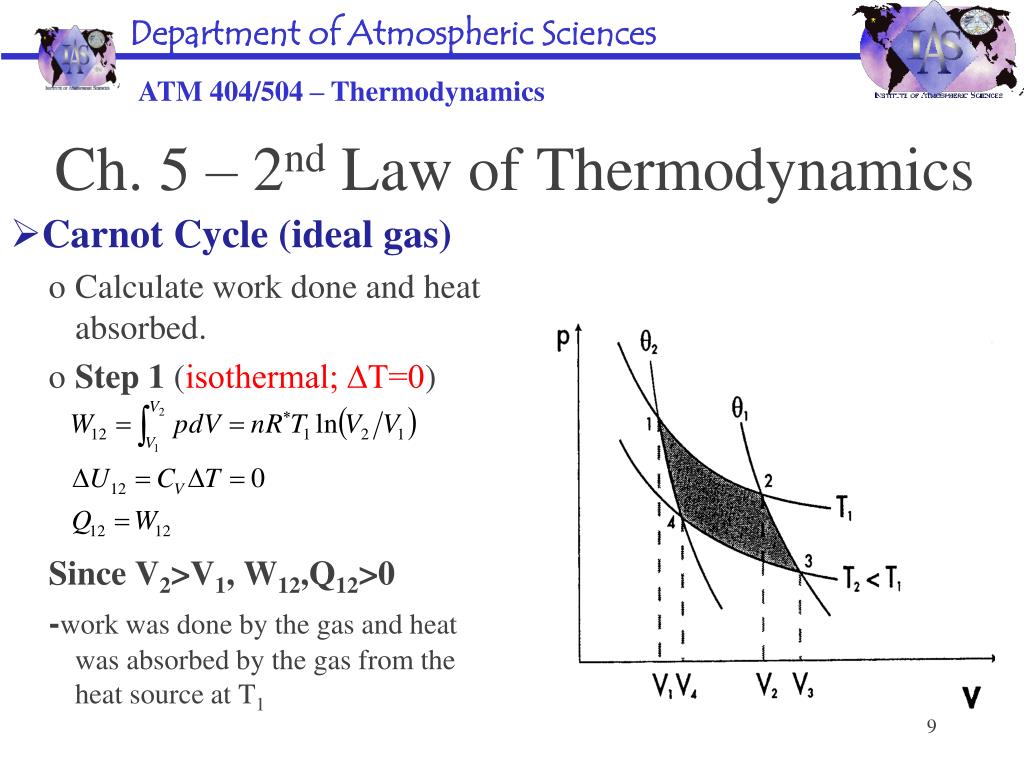
Here we describe the database characteristics and implementation and demonstrate its use.
#Second law of thermodynamics calculator code
The eQuilibrator code is open-source and all thermodynamic source data are freely downloadable in standard formats.

The web interface to eQuilibrator ( ) enables easy calculation of Gibbs energies of compounds and reactions given arbitrary pH, ionic strength and metabolite concentrations. To address this problem, eQuilibrator couples a comprehensive and accurate database of thermodynamic properties of biochemical compounds and reactions with a simple and powerful online search and calculation interface. Even simple thermodynamic questions like ‘how much Gibbs energy is released by ATP hydrolysis at pH 5?’ are complicated excessively by the search for accurate data. However, thermodynamic data on biochemical compounds can be difficult to find and is cumbersome to perform calculations with manually. The laws of thermodynamics constrain the action of biochemical systems.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
